

How to Write a Recount Text (And Improve your Writing Skills)
WHAT IS A RECOUNT TEXT?

The recount text type retells an experience or an event that happened in the past. The purpose of a recount is to inform, entertain, and/or evaluate.
A recount can focus on a specific section of an event or retell the entire story. The events in a recount are usually related to the reader in chronological order; That is, in the order they happened.
Recounts are an excellent genre for emergent writers to cut their teeth on. Written mainly in the past tense, recounts offer younger student-writers the opportunity to tell a story in writing without placing cumbersome demands on their creative abilities to construct a well-structured storyline. To avoid the necessity for any research, personal recounts are often the best place for beginners to start. All they’ll need for their plot is a half-decent memory!
A COMPLETE UNIT ON TEACHING RECOUNT WRITING

MASTER RECOUNT WRITING with this complete EDITABLE UNIT that ensures your students learn how to retell events with accuracy and energy. covering PERSONAL, FACTUAL, LITERARY and HISTORICAL RECOUNTS.
Teach your students to write AMAZING RECOUNTS in various styles with this COMPLETE 78 PAGE UNIT . No preparation is required.
WHAT ARE THE FIVE TYPES OF RECOUNT?
There are many different styles of recounting. Let’s take a look at the five main types before studying the recount text structure and features.
PERSONAL RECOUNT : A Personal Recount text retells an activity in which the writer has been personally involved. Personal recounts often build an intimate relationship between the writer and the reader. Some common types of personal recounts include anecdotes, diary & journal entries, personal letters, etc. While there are some differences, a personal narrative has much in common with a personal recount.

PROCEDURAL RECOUNT: A Procedural Recount records the steps in an investigation or experiment, thereby providing the basis for reported results or findings. A procedural recount records events such as a science experiment or cooking. Procedural recounts present the events chronologically (in the order in which they happened). The purpose of procedural recounts is to inform the audience. They differ somewhat from a traditional procedural text .
FACTUAL / NEWSPAPER RECOUNT / HISTORICAL RECOUNT : Factual Recounts report the particulars of an incident by reconstructing factual information, e.g. police reconstruction of an accident, historical recount, biographical and autobiographical recounts. A factual recount is an objective recount of an actual event by someone not personally involved in the situation. Its purpose is either to inform, entertain or both.

LITERARY RECOUNT: A Literary Recount retells a series of events for the purpose of entertainment. A literary recount is like a factual recount in many regards. Both provide details about what happened, including who was involved, when and where the event occurred, and what may have resulted. A literary recount can be about real or fictional events and characters.
IMAGINATIVE RECOUNT : Applies factual knowledge to an imaginary role to interpret and recount events, e.g. A Day in the Life of a German soldier, How I manned the first mission to the moon. An imaginative recount is retelling events, usually in the first person. This style of recount allows for embellishment beyond facts and events- perfect for creative writing.
STRUCTURE AND FEATURES OF A RECOUNT
Recount structure.
ORIENTATION Explain the who, what, when, and where of the experience in your introduction.
FOCUS Only significant events are included.
CHRONOLOGY Events are described in the sequence in which they occurred.
ORGANIZATION Relevant information is grouped in paragraphs.
INSIGHT Include personal comments, opinions or interpretations of the recounted experience or event.
RECOUNT FEATURES
TENSE First and third person are used most frequently, and recall is always written in the past tense. Present tense can be used for analysis and opinion.
NOUNS Use proper nouns to refer to specific people, places, times and events.
VOICE Both active and passive voice is used in recounts.
CONNECTIVES Use conjunctions and connectives to link events and indicate time sequence.
HOW TO WRITE A RECOUNT
POINTS TO CONSIDER BEFORE WRITING :
Writing a recount text in English is a deeply reflective process. As such, students will want to spend most of their writing time organizing the events, refining the details, and fine-tuning the language. Here are some questions for students to consider before beginning the writing process .
- What are you going to tell your audience? What are you recounting?
- What information will the audience need early in the text?
- What are the important events or parts of the recount you want to describe? In what order will they occur?
- How will you let your readers know the order of events? What language will you use to link the events?
- What other information may it be helpful to include?
- How will you conclude your recount?

Students must recount the who , what , when , and where as the bare minimum. To help them organize their thoughts, encourage the use of graphic organizers and mind maps.
At this point, students should consider some of the questions their audience might ask while reading the recount. For example:
- What occurred?
- Where did it take place?
- When did it occur?
- Who were the main characters/people involved?
- Why did certain things happen?
- How did things happen?
- What were some of the reactions to the events that happened?
- What are the concluding thoughts or ideas?
HOW TO STRUCTURE A RECOUNT IN 5 PARAGRAPHS

In terms of structure, the 5-paragraph/hamburger essay framework is perfect for the beginning writer.
This template suits most nonfiction writing genres and lays out a composition with one introductory paragraph, followed by three body paragraphs and one concluding paragraph. Check out our comprehensive article here to learn more about this effective format.
When used in the context of writing a recount, the 5-paragraph essay will look something like this:
The Orientation: Paragraph 1
In the introductory paragraph, the student will establish the setting and introduce the characters and the topic of the recount.
The Events: Paragraphs 2-4
Using past tense verbs, the student will relate the events in chronological order in the body paragraphs.
The Conclusion: Paragraph 5
In the final paragraph of their recount, the students should typically make some sort of evaluative comment on what they think or how they feel about the events they have just related.
The 5-paragraph essay format is very flexible, as students can easily alter the number of body paragraphs according to their abilities and the complexity of the events they recount.
THE 5 PILLARS OF WRITING A RECOUNT TEXT?
For beginning writers, graphic organizers are extremely helpful tools to assist during the planning process. These can be built around the 5-paragraph essay structure as described above.
Another helpful planning tool to help students plan their recounts is employing The Five Pillars of a Recount .
Essentially, the five pillars comprise five questions students must answer in their recount. These are

- Who? Who are the main characters?
- When? When did the events take place?
- Where? Where did the events happen?
- What? What happened?
- Why? Why do these events matter?
The student will have a basic outline for writing their recount by answering each of these questions.
While the who , the when , and the where are usually addressed in the orientation or introductory paragraph, the what will be taken care of in the body paragraphs, with the why most often providing the focus for the concluding paragraph.
TIPS FOR WRITING A GREAT RECOUNT TEXT
- Keep the title simple to summarise the text’s central element, such as “ A trip to the Zoo.”
- Set the scene for the audience in terms of characters, setting and context. We refer to this as our orientation, and it will provide the reader with all the essential ingredients of the recount in the introduction by addressing the who, what, when and where.
- Keep everything in chronological order in a recount and use a variety of time transitional terms and phrases to keep your audience engaged throughout.
- Use a range of adjectives; try and avoid “And then, and then, and then.”
- Each new section will require a new paragraph. Be sure to check out our Every new section will require a new paragraph. Be sure to check out our own complete guide to writing perfect paragraphs here.
- Use the correct language and terms relevant to your recount. Consider your audience and the language they will connect with.
- If you are writing from a specific point of view , use the relevant language to match the perspective. Most commonly, in a recount, you will be recounting in the first person.
- Recounts are always written in the past tense, so be conscious of staying in this tense throughout. Everything has already happened, so ensure your vocabulary reflects this.
- The challenge in writing a good recount is to provide the audience with the story as it happened but to leave out incidental and dull information.
- Ensure you also clearly understand your audience, as this will significantly impact the language you use.

Tools & Resources
Use your students’ resources and tools below to improve their writing skills through proven teaching strategies.
RECOUNT TEXT GRAPHIC ORGANIZER

RECOUNT WRITING PROMPTS AND TOPICS
Often, the topic of the recount will suggest itself in the form of a title. Recounts are great for forging cross-curricular links with other subjects. For example, you may want your students to write a historical recount on a topic they covered in social studies or create a procedural recount on an experiment they completed in science.
Generally, a recount’s focus is summed up in the title. For personal recounts, providing students with a title as a prompt is a great way to get the ball rolling without being too prescriptive, as it will still be up to the student to select the specific events they write about.
Here are a few ideas for titles for personal recounts:
- My Most Magical Moment Ever
- A Moment I Will Never Forget
- A Moment I Will Always Regret
- A Trip with My Best Friend
- My Favorite Memory
- The Biggest Surprise of My Life
- My Proudest Achievement
You’ll find more recount writing prompts for students below.

Recount Writing Example (Student Writing Samples)
Below is an annotated recount text example and student samples. Click on the image to enlarge and explore them in greater detail. Please take a moment to both read the different styles of recounting text in detail and also the teacher and student guides which highlight some of the critical elements of a recount to consider before writing.
Please understand these student writing samples are not intended to be perfect examples for each age or grade level but a piece of writing for students and teachers to explore together to critically analyze to improve student writing skills and deepen their understanding of recount writing.
We would recommend reading the example either a year above or below, as well as the grade you are currently working with, to gain a broader appreciation of this text type .
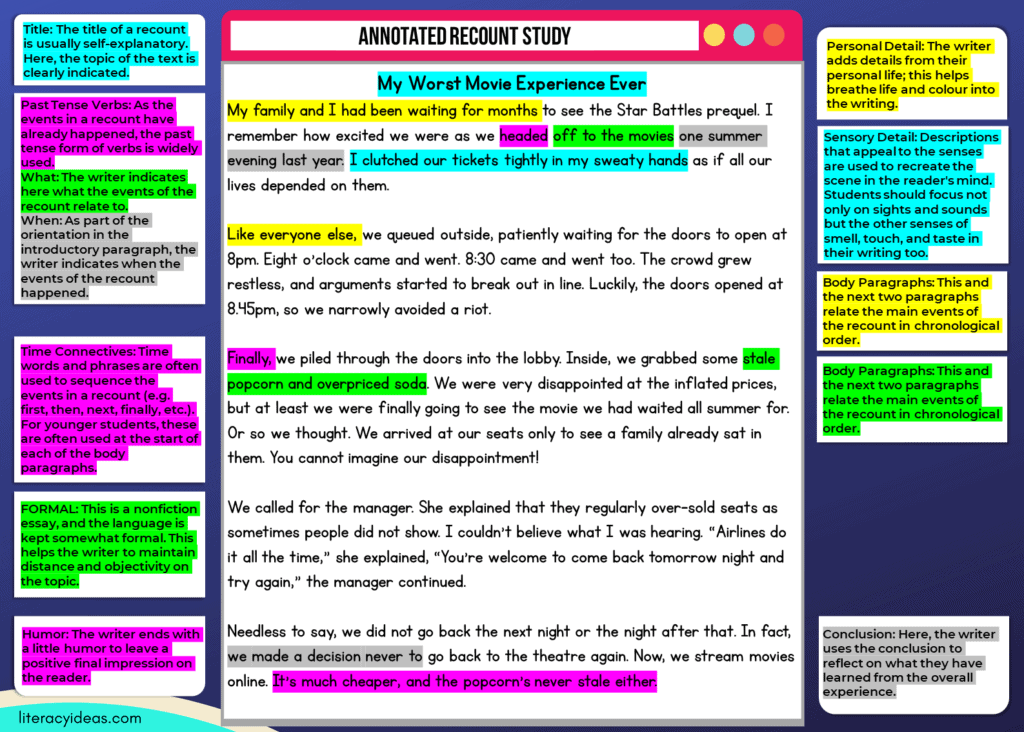
RECOUNT TEACHING RESOURCES
Easy recount writing activities for students.
ACTIVITY ONE: A SHARED VISUAL RECOUNT
Provide an image of a significant event all students could recount as a group. For example, this could be a school camp, the Olympic games, or a photo of a significant event within your community. Get students to work through the Who ? When ? Where ? What ? and Why ?
Once you have established these, students can start to place things in chronological order and prioritize what will be included in their recount draft.
At this point, get your students to collaborate on a recount of this shared event. You can use these as a starting point for comparison and analysis before students write their individual recounts.
ACTIVITY TWO: BUDDING JOURNALIST RECOUNTS
First, find a suitable video or a newspaper article. Set your students the task of taking notes on the KEY information. Make it clear to your students that they are writing a BRIEF newspaper article to share information with others and that personal opinions are not required for this task. The aim is to provide the audience with enough information to make their own opinions and inferences .
Let your students read or watch the article or video a maximum of twice. Notes should be brief. They are not trying to recreate the entire script or article.
When they have finished, check the chronology of their recounts. How successful were they in recounting the events in order?
ACTIVITY THREE: PAIRED FLOWCHARTS
When your students have created their own individual recounts, get them to share them with a partner. During this time, the reader will develop a flowchart of what happened and, if appropriate, be able to explain an action/reaction process, such as “You ate so much cake at your party that later that night, you got sick.”
By completing this conferencing process, students will hear first-hand if their recount makes sense to others.
RECOUNT WRITING CHECKLIST BUNDLE

⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ (92 Reviews)
MORE GREAT RECOUNT WRITING ARTICLES

How to Write a Historical Recount Text

5 Easy Recount Writing Lesson Plans students love.

15 Awesome Recount & Personal Narrative Topics

Explore our Premium Teaching Unit on RECOUNT WRITING
Get Daily Travel Tips & Deals!
By proceeding, you agree to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .

Write a Good Travel Essay. Please.
Kathleen Boardman
Travel Smarter! Sign up for our free newsletter.
Editor’s Note: We know that many of you are looking for help writing travel experience essays for school or simply writing about a trip for your friends or family. To inspire you and help you write your next trip essay—whether it’s an essay about a trip with family or simply a way to remember your best trip ever (so far)—we enlisted the help of Professor Kathleen Boardman, whose decades of teaching have helped many college students learn the fine art of autobiography and life writing. Here’s advice on how to turn a simple “my best trip” essay into a story that will inspire others to explore the world.
Welcome home! Now that you’re back from your trip, you’d like to share it with others in a travel essay. You’re a good writer and a good editor of your work, but you’ve never tried travel writing before. As your potential reader, I have some advice and some requests for you as you write your travel experience essay.
Trip Essays: What to Avoid
Please don’t tell me everything about your trip. I don’t want to know your travel schedule or the names of all the castles or restaurants you visited. I don’t care about the plane trip that got you there (unless, of course, that trip is the story).
I have a friend who, when I return from a trip, never asks me, “How was your trip?” She knows that I would give her a long, rambling answer: “… and then … and then … and then.” So instead, she says, “Tell me about one thing that really stood out for you.” That’s what I’d like you to do in this travel essay you’re writing.
The Power of Compelling Scenes
One or two “snapshots” are enough—but make them great. Many good writers jump right into the middle of their account with a vivid written “snapshot” of an important scene. Then, having aroused their readers’ interest or curiosity, they fill in the story or background. I think this technique works great for travel writing; at least, I would rather enjoy a vivid snapshot than read through a day-to-day summary of somebody’s travel journal.
Write About a Trip Using Vivid Descriptions
Take your time. Tell a story. So what if you saw things that were “incredible,” did things that were “amazing,” observed actions that you thought “weird”? These words don’t mean anything to me unless you show me, in a story or a vivid description, the experience that made you want to use those adjectives.
I’d like to see the place, the people, or the journey through your eyes, not someone else’s. Please don’t rewrite someone else’s account of visiting the place. Please don’t try to imitate a travel guide or travelogue or someone’s blog or Facebook entry. You are not writing a real travel essay unless you are describing, as clearly and honestly as possible, yourself in the place you visited. What did you see, hear, taste, say? Don’t worry if your “take” on your experience doesn’t match what everyone else says about it. (I’ve already read what THEY have to say.)
The Importance of Self-Editing Your Trip Essay
Don’t give me your first draft to read. Instead, set it aside and then reread it. Reread it again. Where might I need more explanation? What parts of your account are likely to confuse me? (After all, I wasn’t there.) Where might you be wasting my time by repeating or rambling on about something you’ve already told me?
Make me feel, make me laugh, help me learn something. But don’t overdo it: Please don’t preach to me about broadening my horizons or understanding other cultures. Instead, let me in on your feelings, your change of heart and mind, even your fear and uncertainty, as you confronted something you’d never experienced before. If you can, surprise me with something I didn’t know or couldn’t have suspected.
You Can Do It: Turning Your Trip into a Great Travel Experience Essay
I hope you will take yourself seriously as a traveler and as a writer. Through what—and how—you write about just a small portion of your travel experience, show me that you are an interesting, thoughtful, observant person. I will come back to you, begging for more of your travel essays.
Take Notes in a Cute Journal

Keep track of all the crucial details- and even the ones you might forget, in a durable and refillable journal.
More from SmarterTravel:
- Genealogy Travel: How to Find Your Family Tree
- The Essential International Packing List
- 9 DIY Ways to Upgrade Economy Class
We hand-pick everything we recommend and select items through testing and reviews. Some products are sent to us free of charge with no incentive to offer a favorable review. We offer our unbiased opinions and do not accept compensation to review products. All items are in stock and prices are accurate at the time of publication. If you buy something through our links, we may earn a commission.
Top Fares From

Don't see a fare you like? View all flight deals from your city.
Today's top travel deals.
Brought to you by ShermansTravel
Greece: 8-Nt, Small-Group Tour, Incl. Aegina,...

Amsterdam to Copenhagen: Luxe, 18-Night Northern...
Regent Seven Seas Cruises

Ohio: Daily Car Rentals from Cincinnati

Trending on SmarterTravel
Trending Post : 52 Best Things to do in Ireland

Great Travel Writing Examples from World Renowned Travel Writers
Are you ready to be a better travel writer? One of the best ways to do this is to read great travel writing examples from great travel writers.
Writing about travel in a way that keeps your reader reading is not always easy. Knowing how to write an irresistible first paragraph to entice the reader to keep reading is key. Writing a lede paragraph that convinces the reader to finish the article, story or book is great travel writing. This article features travel writing examples from award-winning travel writers, top-selling books, New York Times travel writers, and award-winning travel blogs.
Ads are how we pay our bills and keep our blog free for you to enjoy. We also use affiliate links; if you make a purchase through them, we may receive a small commission at no cost to you.

The writers featured in this article are some of my personal favorite travel writers. I am lucky to have met most of them in person and even luckier to consider many friends. Many I have interviewed on my podcast and have learned writing tips from their years of travel writing, editing and wisdom.
11 Great Travel Writing Examples
Writing with feeling, tone, and point of view creates a compelling story. Below are examples of travel writing that include; first paragraphs, middle paragraphs, and final paragraphs for both travel articles as well as travel books.
I hope the below examples of travel writing inspire you to write more, study great travel writing and take your writing to a higher level.
Writing Example of a Travel Book Closing Paragraphs

Don George is the author of the award-winning anthology The Way of Wanderlust: The Best Travel Writing of Don George , and the best-selling travel writing guide in the world: How to Be a Travel Writer .
He is currently Editor at Large for National Geographic Travel, and has been Travel Editor at the San Francisco Examiner-Chronicle, Salon, and Lonely Planet.
I had the wonderful opportunity to see Don speak at Tbex and read from one of his books as well as interview him on the Break Into Travel Writing podcast. You can listen to the full podcast here .
Below is the closing of Don’s ebook: Wanderlust in the Time of Coronavirus: Dispatches from a Year of Traveling Close to Home
I continued hiking up to Lost Trail and then along Canopy View Trail. Around noon I serendipitously came upon a bench by the side of the trail, parked my backpack, and unpacked my lunch. Along with my sandwiches and carrot sticks, I feasted on the tranquility and serenity, the sequoia-swabbed purity of the air, the bird and brook sounds and sun-baked earth and pine needle smells, the sunlight slanting through the branches, the bright patch of blue sky beyond.
At one point I thought of shinrin-yoku, forest bathing, the Japanese practice that has become widely popular in the U.S. This was a perfect example of shinrin-yoku, I thought: Here I am, alone in this forest, immersed in the sense and spirit of these old-growth redwoods, taking in their tranquility and timelessness, losing myself to their sheer size and age and their wild wisdom that fills the air.
I sat there for an hour, and let all the trials, tremors, and tribulations of the world I had left in the parking lot drift away. I felt grounded, calm, quiet—earth-bound, forest-embraced.
In another hour, or two, I would walk back to the main paved trail, where other pilgrims would be exclaiming in awe at the sacred sequoias, just as I had earlier that day.
But for now, I was content to root right here, on this blessed bench in the middle of nowhere, or rather, in the middle of everywhere, the wind whooshing through me, bird-chirps strung from my boughs, toes spreading under scratchy pine needles into hard-packed earth, sun-warmed canopy reaching for the sky, aging trunk textured by time, deep-pulsing, in the heart of Muir Woods.
- You can read the whole story here: Old Growth: Hiking into the Heart of Muir Woods
- Please also download Don’s free ebook here: Wanderlust in the Time of Coronavirus
- In addition to writing and editing, Don speaks at conferences, lectures on tours around the world, and teaches travel writing workshops through www.bookpassage.com .

Writing Example of a Travel Book Intro Paragraphs
Francis tapon.

Francis Tapon , author of Hike Your Own Hike and The Hidden Europe , also created a TV series and book called The Unseen Africa, which is based on his five-year journey across all 54 African countries.
He is a three-time TEDx speaker. His social media username is always FTapon. I interviewed Francis on the Break Into Travel Writing podcast about “How to Find An Original Point of View as a Travel Writer “. You can listen to the full podcast here .
Below is the opening of Francis’ book, The Hidden Europe:
“This would be a pretty lousy way to die,” I thought.
I was locked in an outhouse with no way out. Outhouses sometimes have two latches—one on the outside and one on the inside. The outside latch keeps the door shut to prevent rodents and other creatures who like hanging out in crap from coming in. Somehow, that outer latch accidentally closed, thereby locking me in this smelly toilet. I was wearing a thin rain jacket. The temperature was rapidly dropping.
“This stinks,” I mumbled. It was midnight, I was above the Arctic Circle, and the temperatures at night would be just above freezing. There was no one around for kilometers. If I didn’t get out, I could freeze to death in this tiny, smelly, fly-infested shithole.
My mom would kill me if I died so disgracefully. She would observe that when Elvis died next to a toilet, he was in Graceland. I, on the other hand, was in Finland, not far from Santa Claus. This Nordic country was a jump board for visiting all 25 nations in Eastern Europe.
You can find his book on Amazon: The Hidden Europe: What Eastern Europeans Can Teach Us
For $2 a month, you can get Francis’ book as he writes it: Patreon.com/ftapon
Intro (Lede) Paragraph Examples of Great Travel Writing Articles
Michele peterson.

Former banking executive Michele Peterson is a multi-award-winning travel and food writer who divides her time between Canada, Guatemala, and Mexico (or the nearest tropical beach).
Former banking executive Michele Peterson is a multi-award-winning travel and food writer who divides her time between Canada, Guatemala, and Mexico (or the nearest tropical beach). Her writing has appeared in Lonely Planet’s Mexico from the Source cookbook, National Geographic Traveler, Conde Nast’s Gold List, the Globe and Mail, Fifty-five Plus and more than 100 other online and print publications.
She blogs about world cuisine and sun destinations at A Taste for Travel website. I met Michele on my first media trip that took place in Nova Scotia, Canada. I also had the pleasure of interviewing about “ Why the Odds are in Your Favor if you Want to Become a Travel Writer” . You can listen to the full podcast here .
Michele’s Lede Paragraph Travel Writing Example
I’m hiking through a forest of oak trees following a farmer who is bleating like a pied piper. Emerging from a gully is a herd of black Iberian pigs, snuffling in response. If they weren’t so focused on following the swineherd, I would run for the hills. These pigs look nothing like the pink-cheeked Babe of Hollywood fame.
These are the world’s original swine, with lineage dating back to the Paleolithic Stone Age period where the earliest humans decorated Spain’s caves with images of wild boars. Their powerful hoofs stab the earth as they devour their prized food, the Spanish bellota acorn, as fast as the farmer can shake them from the tree with his long wooden staff. My experience is part of a culinary journey exploring the secrets of producingjamón ibérico de Bellota, one of the world’s finest hams.
You can read the full article here: Hunting for Jamón in Spain
Perry Garfinkel

Perry Garfinkel has been a journalist and author for an unbelievable 40 years, except for some years of defection into media/PR communications and consulting.
He is a contributor to The New York Times since the late ’80s, writing for many sections and departments. He has been an editor for, among others, the Boston Globe, the Middlesex News, and the Martha’s Vineyard Times.
He’s the author of the national bestseller “ Buddha or Bust: In Search of the Truth, Meaning, Happiness and the Man Who Found Them All ” and “ Travel Writing for Profit and Pleasure “.
Perry has been a guest on my podcast twice. He gave a “ Master Class in Travel Writing ” you can listen to the full podcast here . He also shared “ How to Find Your Point Of View as a Travel Writer ” you can listen to the full episode here .

Perry’s Lede Travel Article Example from the New York Times
SAN FRANCISCO — A block off Grant Avenue in San Francisco’s Chinatown – beyond the well-worn path tourists take past souvenir shops, restaurants and a dive saloon called the Buddha Bar – begins a historical tour of a more spiritual nature. Duck into a nondescript doorway at 125 Waverly Place, ascend five narrow flights and step into the first and oldest Buddhist temple in the United States.
At the Tien Hau Temple, before an intricately carved gilded wooden shrine and ornate Buddha statues, under dozens of paper lanterns, Buddhists in the Chinese tradition still burn pungent incense and leave offerings to the goddess Tien Hau in return for the promise of happiness and a long life.
You can read the full article here: Taking a Buddhist pilgrimage in San Francisco
Elaine Masters

Elaine Masters apologizes for pissing off fellow travelers while tracking story ideas, cultural clues, and inspiring images but can’t resist ducking in doorways or talking with strangers.
She’s recently been spotted driving her hybrid around the North American West Coast and diving cenotes in the Yucatan. Founder of Tripwellgal.com, Elaine covers mindful travel, local food, overlooked destinations and experiences. Elaine was a guest on my podcast where we spoke about “ How to Master the CVB Relationship “. You can listen to the full podcast here .
Elaine’s Lede Example
I jiggered my luggage onto the escalator crawling up to the street. As it rose into the afternoon light, an immense shadow rose over my shoulder. Stepping onto the sidewalk, I burst into giggles, looking like a madwoman, laughing alone on the busy Barcelona boulevard. The shadow looming overhead was the Sagrada Familia Cathedral. It had mesmerized me forty years earlier and it was the reason I’d finally returned to Spain.
You can read the full article here: Don’t Miss Going Inside Sagrada Familia, Barcelona’s Beloved Cathedral

Along with his wife, photographer Mary Gabbett, Bret Love is the Co-Founder/Editor In Chief of Green Global Travel and the Blue Ridge Mountains Travel Guide.
He’s also an award-winning writer whose work has been featured by more than 100 publications around the world, including National Geographic, Rolling Stone, American Way, the Washington Post, and the New York Times.
Bret’s Lede Example
Congo Square is quiet now. Traffic forms a dull drone in the distance. A lone percussionist taps out ancient tribal rhythms on a two-headed drum. An air compressor from Rampart Street road construction provides perfectly syncopated whooshes of accompaniment.
Shaded park benches are surrounded by blooming azaleas, magnolias, and massive live oaks that stretch to provide relief from the blazing midday sun. It’s an oasis of solitude directly across the street from the French Quarter.
Congo Square is quiet now. But it’s here that the seeds of American culture as we know it were sown more than 200 years ago. And the scents, sounds, and sights that originated here have never been more vital to New Orleans than they are now, more than a decade after Hurricane Katrina devastated the city.
You can read the full article here: Treme, New Orleans (How Congo Square Was The Birthplace Of American Culture)
Middle Paragraph Examples of Great Travel Writing Articles
Mariellen ward.

Canadian travel writer and blogger Mariellen Ward runs the award-winning travel site Breathedreamgo.com , inspired by her extensive travels in India.
She has been published in leading media outlets worldwide and offers custom tours to India through her company India for Beginners. Though Canadian by birth, Mariellen considers India to be her “soul culture” and she is passionate about encouraging mindful travel.
Mariellen’s Middle Paragraph Example
While the festival atmosphere swirled around me, I imbued my diya with hope for personal transformation. I had come to India because a river of loss had run through my life, and I had struggled with grief, despair and depression for eight years. I felt I was clinging to the bank, but the effort was wearing me out. Deciding to leave my life and go to India was like letting go of the bank and going with the flow of the river. I had no idea where it would lead me, what I would learn or how I would change. I only knew that it was going to be big.
You can read the full article here: The River: A tale of grief and healing in India

Joe Baur is an author and filmmaker from Cleveland currently based in Berlin. His work has appeared in a variety of international publications, including BBC Travel, National Geographic, and Deutsche Welle.
He regularly reports for the Jewish Telegraphic Agency and is the author of Talking Tico detailing his year of living in Costa Rica and traveling around Central America. I interviewed Joe about “ How to Find Unique Travel Stories “. You can listen to the full podcast here .
Joe Baur’s Middle Paragraph Example
I first became aware of the Harz mountains and the Brocken when reading the works of some of Germany’s great writers, like Goethe and Heinrich Heine. Legends of witches congregating with the devil being the main theme of the mountain’s mythology. I, however, was more interested in a refreshing time spent in nature rather than reveling with the devil.
The first stage from Osterode to Buntenbock was a warm-up to the more rigorous stages ahead. It began on sidewalks before sliding into the forest sporting a healthy shade of green — a gentle jaunt that made my hiking boots feel a bit like overkill given the dry, pleasant weather.
You can read the full article here: Follow the witch through the forest: 5 days hiking Germany’s Harz
Samantha Shea

Samantha is a freelance travel writer with bylines in Matador Network, GoNomad and more. She also runs the travel blog Intentional Detours which provides thorough guides and tales related to offbeat adventure travel in South Asia and beyond.
When she’s not writing she enjoys cycling, hiking, the beach, as well as language learning.
Samantha Shea’s Middle Paragraph Example
Suddenly, the spark of a match pulsed through the early-fall afternoon and my head snapped towards the men. Amir touched the flame to an unidentifiable object that seconds later made itself known by the deep earthy scent of Pakistani hashish.
Amir’s ice blue eyes focused intently on his creation: a combination of tobacco and nuggets of greenish-brown charas. He forced the mixture back into the cigarette, before bringing it to his pursed lips, flicking the match, and setting flame to his high.
I reached out from the cot to take my turn and took a deep inhale, acutely pleased. I savored the familiar burn of the drag, the rows and rows of corn and apple plants in front of me, the stuttered cacophony of animal exclamations behind me, and the generosity of the men to my left, some of whom we had just met an hour before.
You can read the full article here: Thall Tales: A Hazy Afternoon in Thall, Pakistan
Final Paragraph Example of Great Travel Writing Articles
Cassie bailey.
Cassie is a travel writer who has solo backpacked around Asia and the Balkans, and is currently based in Auckland. Alongside in-depth destination guides, her blog has a particular focus on storytelling, mental health, and neurodiversity.
Cassie’s Final Paragraphs Example
So my goal is to feel, I guess. And I don’t mean that in a dirty way (although obvz I do mean that in a dirty way too). This is why we travel, right? To taste crazy new foods and to feel the sea breeze against our skin or the burn on the back of our legs on the way down a mountain. We want to feel like shite getting off night buses at 4am and the sting of mosquito bites. We know we’re going to feel lost or frustrated or overwhelmed but we do it anyway. Because we know it’s worth it for the ecstasy of seeing a perfect view or making a new connection or finding shitty wine after a bad day.
My goal is never to become numb to all of this. To never kid myself into settling for less than everything our bodies allow us to perceive. I’m after the full human experience; every bit, every feeling.
You can read the full article here: Goals inspired by life as a solo backpacker
Lydia Carey

Lydia Carey is a freelance writer and translator based out of Mexico City who spends her time mangling the Spanish language, scouring the country for true stories and “researching” every taco stand in her neighborhood.
She is the author of “ Mexico City Streets: La Roma ,” a guide to one of Mexico City’s most eclectic neighborhoods and she chronicles her life in the city on her blog MexicoCityStreets.com .
Lydia’s Final Paragraphs Example
Guys from the barrio huddle around their motorcycles smoking weed and drinking forties. Entire families, each dressed as St. Jude, eat tacos al pastor and grilled corn on a stick. Police stand at a distance, keeping an eye on the crowd but trying not to get too involved.
After this celebration, many of the pilgrims will travel on to Puebla where they will visit some of the religious relics on display in the San Judas church there. But many more will simply go back to their trades—legal and illegal—hoping that their attendance will mean that San Judas protects them for another year, and that he has their back in this monster of a city.
You can read the full article here: San Judas de Tadeo: Mexico’s Defender of Lost Causes

I hope you enjoyed these examples of travel writing and they have inspired you to want to write more and write better! The next article that will be published is a follow-up to this and will include travel writing examples from my first travel writing teacher, Amanda Castleman. This article will include travel writing tips from Amanda and travel writing examples from her students as well as one from her own writing.

Follow 52 Perfect Days on Facebook | Twitter | Pinterest | Instagram
If you liked it, please share it. Thank you!
- Pinterest 1
Alexa Meisler is the editorial director of 52 Perfect Days. Born in Paris, France she has since lived in Chicago, San Francisco, Los Angeles and Portland, Oregon. She currently resides in San Diego with her husband and son where they enjoy exploring California and Mexico.
Travel has always been a part of her life; traveling to such places as Morocco, Tangiers and Spain as a young child as well as taking many road trips to Mexico with her grandparents as a young girl. Since then, she has traveled abroad to locations such as Russia, Taiwan and throughout Europe.
Prior to working at 52 Perfect Days she was a freelance travel writer; focusing on family and women’s adventure experiences.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Autobiographies
How to Write a Personal Recount
Last Updated: January 17, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was reviewed by Gerald Posner . Gerald Posner is an Author & Journalist based in Miami, Florida. With over 35 years of experience, he specializes in investigative journalism, nonfiction books, and editorials. He holds a law degree from UC College of the Law, San Francisco, and a BA in Political Science from the University of California-Berkeley. He’s the author of thirteen books, including several New York Times bestsellers, the winner of the Florida Book Award for General Nonfiction, and has been a finalist for the Pulitzer Prize in History. He was also shortlisted for the Best Business Book of 2020 by the Society for Advancing Business Editing and Writing. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 135,231 times.
Writing a personal recount requires you to retell an activity or event that happened in your own life. You must structure your story in a way that makes sense while using language that matches the same purpose.
Considerations

- The first thing you need to understand is the writing prompt itself. If your teacher asks you to write about a favorite holiday memory, your recount needs to describe something that happened during a holiday. It should not describe a favorite memory that happened in school, after class on a normal school day, or during a normal weekend.
- Pay attention to requirements concerning length, as well. Your teacher may tell you how many words, pages, or paragraphs your recount needs to be. If these instructions are not included and you aren't sure about how long the piece must be, consider asking your teacher directly.

- Most recounts are meant to inform, entertain, or do some combination of the two. Personal recounts are generally written for entertainment, but if your teacher asks you to describe an event he or she was not present for—like what happened during your last sports game or during a time when a substitute teacher led class—you also need to make sure that you provide plenty of accurate information about that event.

- For classroom purposes, your recount will usually be written for either your teacher or your peers. Your teacher will want to see that you followed the instructions he or she provided. Your classmates will usually want to be entertained with a story they can enjoy or relate to.

- For example, if you need or want to write a personal recount about a fun summer memory, you probably shouldn't write about your best friend moving away. As a sad memory, describing the loss of your friend won't create the “fun” mood your recount is supposed to have.

- Choose something simple. For instance, a recount about your favorite pet might be titled, “My Favorite Pet.”

- Identify the participants. Even though a personal recount must retell a story from your own life, other people will probably be involved in your story, too. Mentioning these individuals early on will prevent the reader from being surprised or confused later.
- Explain when the activity happened and where it happened, as well. These details are crucial if you want your readers to understand the events of your story.
- For example, if you choose to write about a beach vacation spent with your family, consider starting with something like, “I spent the first week of July with my mother, father, sister, Uncle Eric, and Aunt Lydia. We stayed at a hotel on the beach.”

- For instance, if school was canceled for the day because of a major blizzard, you should mention the blizzard first, followed by the discovery that school was canceled. Write about what you did with your day off only after explaining why you had that day off.

- As a general rule, only describe events that the reader would not be able to predict. When writing a personal recount about your weekend, you could describe the games you played, the people you met with, and any special treats you may have enjoyed. You do not need to explain that you went to sleep each night or ate breakfast each morning, however, since those are things your teacher expects you to do every weekend.

- For personal recounts that cover an extended period of time, each paragraph might describe one easily separated portion of that time. A recount about your weekend might include one paragraph for Friday evening, one paragraph for Saturday, and one paragraph for Sunday. A recount about your summer might include one paragraph for May, one paragraph for June, one paragraph for July, and one paragraph for August.

- This is especially important when you are writing a personal recount about someone or something important. Personal recounts about your favorite pet should include a description of how your pet looks. Personal recounts about your grandparents should include descriptions of how your grandparents look and sound.

- Consider including a personal opinion about what happened. For instance, you might say conclude a personal recount about your Christmas with a statement like, “This past Christmas was very fun.”
- You may also need to conclude by describing the outcome of the activity. If you are telling a recount about your visit to the doctor, end with an explanation of what your doctor told you or what medicine he or she gave you. [3] X Research source

- For a personal recount, you need to describe how you felt and what you did. Doing this will be impossible if you do not tell the story from your perspective.

- The words “played,” “raced,” and “painted” describe the actions you and your cousin performed.
- It makes more sense to say that you performed these actions than to describe these events without saying anything about doing them. A description of the park you raced to won't make sense if you don't first explain that you raced to it.

- This means converting all of your verbs to the past tense. Instead of saying that you “enjoy” eating at your favorite restaurant, you will need to write that you “enjoyed” eating at your favorite restaurant.
- For most verbs, you can change them to the past tense by add “-ed” to the end of the verb. Examples include: enjoyed (enjoy), played (play), visited (visit), walked (walk)
- For some verbs, several letters within the word will change and no “-ed” is needed. A few common examples include: ran (run), ate (eat), went (go)

- Transitions describe the order of events. A few examples include: first, next, later, meanwhile, then, finally
- First , I did _________.
- Next , we went to the ______.
- Later , I decided to ______.
- Meanwhile , my parents were ______.
- Then , all of us ______.
- Finally , we ended the day by ______.
Community Q&A
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://englishonline.tki.org.nz/English-Online/Planning-for-my-students-needs/Resources-research-and-professional-support/Features-of-text-forms/Recounts
- ↑ https://www.ziptales.com/pdfs/scripts/write-recount.pdf
About This Article

- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Antonio Criscione
Jun 6, 2016
Did this article help you?

Ismail Khan
Oct 14, 2016
Aug 24, 2018
Mar 1, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
6 examples of gorgeous travel writing
Inspiration to help your next travel blog, guidebook, or article stand out from the crowd.

We live on a wondrous, ever-changing planet— from alpine lakes and cloud forests to ancient cobblestoned cities.
The best travel writers can transport readers to these far-flung destinations, and to introduce them to new cultures and experiences. Good travel writing can be an insightful, thought-provoking, and even life-changing genre.
And with interactive content platforms, it’s possible for travel writers to create truly immersive reading experiences online. In this guide, we introduce six ideas — and examples of travel writing — to help you create beautiful, interactive travel stories.
Whether you're a beginner travel writer, a publisher, destination marketer, or freelance travel blogger, we've got plenty of inspiration to get you started.
What do the BBC, Tripadvisor, and Penguin have in common? They craft stunning, interactive web content with Shorthand. And so can you! Publish your first story — no code or web design skills required. Sign up now.
The features of great travel writing

The best travel writing is unique, but there are still some general guidelines you’ll want to follow to make your travel writing stand out from the pack. Here are some travel writing tips to help you compete with the best examples of the genre.
- Have a point of view. Great travel writers — from the travel books of Bill Bryson and John Steinbeck to the documentaries of Paul Theroux — all have very specific points of view that are difficult to copy. Find your voice, and your travel articles will truly sing.
- Take great photos. The best travel writing is visually immersive, using high resolution images and video to engage the reader’s senses. Even if you’re not creating a photo essay , modern travel writing relies of great visual assets.
- Use multimedia content where you can. If you can, create audio and video assets, too, and consider building out your story with a digital storytelling platform to use interactive features. Embed podcasts and clips to keep the reader engaged.
- Learn from the best. Keep track of longform feature stories in the New York Times and the Washington Post, and steal their techniques. (Good travel writers borrow, great travel writers steal, to butcher TS Eliot.)
- Create a beautiful web presence. We love the print Lonely Planet travel guides, but these days you need to produce stunningly engaging content on the web. Standards are high, but you’d be amazed what you can do with modern interactive content platforms.
- Provide a sense of adventure — even if you’re not strictly doing ‘adventure travel’. Whether you’re writing a first person travel memoir or writing about your backpacker’s trip through the Amazon, you want to keep your reader engaged with your travel experiences.
- Make it educational. Teach the reader something new about the world they’re exploring.
- Edit your work. The best travel writers kill their darlings and pay attention to details — hello, commas — knowing that this is how the best work is created.
Want to improve the efficiency of your writing process? Check out our list of the best writing tools .

Inspire readers and move them to action by exploring a location's unique history and culture. By focusing on just one place, your readers get the chance to experience it deeply through your words and imagery.
Intrepid Travel's Shorthand story 'Welcome to Olkola Country' is simple, yet effective. The highlight of the story is its elegant writing — a blend of reporting and personal narrative that explores the history, culture, and ecology of an ancestral land of the Olkola people in Australia. The story is elevated with thoughtful photos and videos, and ends with a call to action for the newly-inspired reader.
Looking for more inspiration? Check out our roundup of ten stunning photo essay examples .
The right images can make a story feel polished and inspired.
2 . Time travel

Taking readers back through historical moments is a great way to achieve more depth in your stories.
In the story The Museum of Atari, Mario and Electronic Childhood Dreams , Channel News Asia uses Shorthand to create a stunning visual story about a little-known museum of retro video games in Singapore. The highlight of the story is an interactive scrollytelling timeline about the history of video games, which is created using the Shorthand Reveal feature and animates a pixel character as the reader scrolls.
Our Reveal section allows animations like this to be controlled by the reader's scrolling.
3 . Immerse your reader

When words and photos simply aren't enough to convey the complexity of a travel story, add another layer of reader engagement using various forms of media.
The Sydney Opera House story A Guide to Dance Rites uses multimedia to bring indigenous culture to life. With elements like animation, slideshows, and embedded audio clips, readers can feel fully immersed in one of Australia's most traditional dance competitions.
Embed your own code to add further customisation to your story.
With Shorthand, remember that you always have the option to add custom HTML to add further customisations to your stories. See a list of our recommended third party tools in this support document .
4 . Keep it practical

Travel stories don't always need to inspire wanderlust or transport readers to far-flung destinations. Some of the most effective and important travel stories simply provide practical advice — whether that's how to exchange currency, say 'thank you' in a foreign language, or avoid danger.
Travel Weekly's story Traveling While Female explores how female travellers can stay safe, and uses data to stress the importance of improving women's safety abroad. By displaying the data as interactive graphics, Travel Weekly draws extra emphasis to key statistics.
Make your data memorable by giving it special emphasis.
5. Zoom out

When you've written a couple of beautiful travel stories, what's next?
Tie together your creative vision by consolidating your stories into a single landing page. You can use Shorthand to create a home for all of your stories, whether that's by using our Collection section or by including links in other section types.
For example, Luxury Travel nests all of its feature content within a Shorthand story. The page takes advantage of our media-rich sections to create a scrolling archive of their beautiful travel stories.
Consolidate your features in a single Shorthand story.
There are myriad ways to turn a Shorthand story into a landing page. Here's another example from Perth Now, which takes a simple, colourful approach.
There are many ways to customise a Shorthand story to serve as a landing page.
4 . Just the highlights

Not every trip allows for the luxury of time. In order to get the point across, sometimes a quick and to-the-point listicle is all that's necessary to deliver a clear and time-efficient message.
Creating a unique online travel story can seem like a daunting task, but Shorthand's many easy-to-use features exist to help make your stories exceptional. There are thousands of destinations waiting to be written about, and we can't wait to see where your stories take us next.
Add The Craft to your inbox
Receive storytelling tips from The Craft and the most amazing Shorthand stories from around the web, hand selected by our team, every two weeks.
Example: Recount
A Trip to the National Zoo and Aquarium
Yesterday, my family and I went to the National Zoo and Aquarium to visit the new Snow Cubs and the other animals.
In the morning, when we got to the Zoo and Aquarium there was a great big line, so we had to wait awhile to get in.
After we entered the zoo, we went straight to the enclosure for the Snow Cubs. My brother and I were so excited to see them. They were so cute and playful. At lunchtime Dad decided to cook a bbq. He cooked sausages so we could have sausage sandwiches. Mum forgot the tomato sauce so we had to eat them plain.
In the afternoon, we visited the aquarium. My brother was excited to see the sharks and the tropical fish. At the end of the day when we left we were going to go and get ice cream but we decided we were too tired so we drove straight home. (First steps 1st edition p47)
- Memberships
- School packages
- Free resources
- Get started for free
- Free writing resources
- About Seven Steps
- What is the Seven Steps?
- Evidence-based approach
- Seven Steps and the Curriculum
- Impact Report
- Success Stories
- Press & Media
- Narrative Writing
- Persuasive Writing
- Informative Writing
No products in the cart.

- Your password must be 8 or more characters, including at least 1 upper case letter, 1 lower case letter and 1 number.
- Add new school
How to teach your students to write a captivating holiday recount

It’s hot and sticky, your eyelids weigh as much as a cinderblock and you have to read page after page of, ‘In the holidays…’ followed by a blow-by-blow account of everything students did.
As a teacher, you may have 99 problems but let’s make sure boring holiday recounts are not one of them!
One of the main reasons students all write the same boring recounts is because they are simply writing down everything that comes to mind.
The solution is to think first, write second .
As with any piece of writing, brainstorming ideas before you start writing is the best way to ensure that your writing is original and engaging.
What makes a captivating holiday recount?
Have a read of the following recount:
“Beep” “Squeak” “Come on!” This is the fifth time in a traffic jam and we’re still two hours away from camp.
When we finally arrive, my Dad is relieved that we get there just in time to set up in perfect light. I really love helping Dad set up the tents on the inside.
Oh no! I’ve forgotten my sleeping bag! – Lyla, Year 2
Holiday recounts shouldn’t run through every moment from the second students leave school to the night before coming back.
Students should be writing about the most interesting events and bringing them to life with descriptive language.
Have students use their senses to paint word pictures to engage the reader. It makes their readers feel like they are right there in the moment.
This approach also helps students focus on the most interesting parts of their holiday rather than just giving a blow-by-blow account of everything they did.
How do we create captivating stories and recounts?
Activity: Deconstructed Recount
A deconstructed recount is a fast and engaging activity to improve your students’ descriptive writing so that they show, rather than tell their reader what they did over the break. Here’s how…
- First, brainstorm. Get your students to brainstorm things they saw, heard, tasted, smelt and felt during the holidays.
- Then, ban the boring. Get students to pick the most interesting example for each sense and use the template provided to write a paragraph about each one.
- Finally, get artistic. Ask your students to draw an image to accompany each paragraph.
- Group activity: Ask students to share their deconstructed recounts in groups. Can the group guess what each person did based on their descriptions?
Template: Deconstructed Recount
- Take recounts to the next level with this simple template that promotes descriptive writing.
- Students write and draw in the template to describe their holidays using the Five + 1 Senses.
STEP Step 5: Show, Don’t Tell PURPOSE Apply RESOURCE TYPE Template YEAR F–10
Looking for more resources for spicing up your students’ recounts?
Check out Teacher Hub’s Resource Library for recount resources such as our Lesson Plan: Write Like a Witness or a Classroom Powerpoint about writing a wild food fight !
Alison Langmaid from Sunrise Christian School in South Australia kindly shared this activity idea and this fantastic example written by one of her Year 2 students. For more examples of captivating recounts read our blog, 4 recounts every teacher wants to read .

For students trained in the Seven Steps, have them use the five paragraphs to construct a complete holiday recount. Prompt students to think about which paragraphs would work well as a Sizzling Start and an Ending with Impact.
Ask: How can they order the paragraphs to build momentum and interest in their recount?
Seven Steps blog
Explore, learn and grow Discover the latest tips and insights >

- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search

Trip Recount Plan and Resources
Subject: English
Age range: 7-11
Resource type: Lesson (complete)
Last updated
24 February 2018
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

A 3 day plan on recount writing - best used to recount a recent trip. Initially planned for Year 3 but could easily be adapted. Included are detailed powerpoints to aid teaching, differentiated activities and plan.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to Write a Recount Text (And Improve your Writing ...
Editor's Note: We know that many of you are looking for help writing travel experience essays for school or simply writing about a trip for your friends or family. To inspire you and help you ...
Recount writing purpose, styles, grammatical features and structure. Recount writing example 'My Summer Holiday'. Writestyler 'Pro' level. Visit https://www....
Great Travel Writing Examples from World Renowned ...
Pay attention to requirements concerning length, as well. Your teacher may tell you how many words, pages, or paragraphs your recount needs to be. If these instructions are not included and you aren't sure about how long the piece must be, consider asking your teacher directly. 2. Understand the purpose.
Dover. When we arrived at the castle, I was amazed at how enormous it was! We parked in the car park and walked up a steep slope into the castle grounds. It felt like the path was almost vertical! Our first activity was. inside the Great Tower, where some actors showed us what medieval life was like at the time of King Henry II.
Middle - the section of something in between the beginning and end. End - the final part of something, such as a story or recount. Fronted adverbial of time - a sentence starter that tells the reader when something happens. Opinion - a personal view about something. Fact - something that is known to be true or proved.
First person - a point of view in writing or storytelling where the narrator or speaker refers to themselves using 'I'. Fronted adverbial of time - a sentence starter that tells the reader when something happens. This piece of writing is based around a school trip to the zoo. You can adapt this lesson to suit wherever you have been recently on ...
Writing the middle and end of a school trip recount. I can write a recount. 1 Slide deck. 1 Worksheet. 2 Quizzes. 1 Video. Free lessons and teaching resources about school trip: writing a recount.
6 examples of gorgeous travel writing - Shorthand
At lunchtime Dad decided to cook a bbq. He cooked sausages so we could have sausage sandwiches. Mum forgot the tomato sauce so we had to eat them plain. In the afternoon, we visited the aquarium. My brother was excited to see the sharks and the tropical fish. At the end of the day when we left we were going to go and get ice cream but we ...
Here's how…. First, brainstorm. Get your students to brainstorm things they saw, heard, tasted, smelt and felt during the holidays. Then, ban the boring. Get students to pick the most interesting example for each sense and use the template provided to write a paragraph about each one. Finally, get artistic.
Writing a recount about a trip can sometimes be quite tricky. This template will help keep children focussed on key information about their day out. Children can use this template to make notes and plan or to write up a finished piece that would look marvellous up on display. The headings give opportunity to reflect on the day out and appreciate what was experienced and learned.
You can also give a rating out of 10 or out of 100% if you want to. A travel recount is something you write about a place that you visited in the past. A travel recount paragraph is structured using 3 different types of sentences: Narrative, which says what you did and describes scenery; fact, which is information about the location; opinion ...
Key learning points. A recount will involve you describing events and experiences in detail. An expanded noun phrase is a group of words with no verb that adds detail to a noun. Expanded noun phrases contain two adjectives, separated by a comma. When we write a plan, we use notes.
Instantly access Twinkl's printable and digital K-12 teaching resources, including worksheets, eBooks, games, PowerPoints, Google Slides, and more!
Trip Recount Plan and Resources. Hi! Have a look at my resources for a range of different subjects, these can be bought as a one off lesson plan including resources or whole unit/term plans including resources and teaching aids. All lessons and resources are aimed at primary age, mainly Year 3 and 4 however can be adapted accordingly.
A helpful, differentiated text to use alongside the teaching of recounts. Be sure to also check out our How to Write a Recount PowerPoint. Twinkl Twinkl Ireland Resources English Medium Schools 3rd/4th Class English Writing Genre/Creative Writing Recount Writing. recount writing recount writing examples recount recount example recount examples ...
This helpful set of Summer Holiday Recount Examples for KS2 will let your students describe their activities over the break. They are the perfect accompaniment to use alongside your teaching on the recount genre of writing. The examples in this pack are differentiated, meaning that they are suitable for students of higher and lower abilities.
I can make a plan for writing a recount about a school trip. 1 Slide deck. 1 Worksheet. 2 Quizzes. 1 Video. 3. 3. Writing a recount about a school trip. I can write a recount about a school trip. 1 Slide deck. 1 Worksheet. 2 Quizzes. 1 Video. Pupils. Learn online. Teachers. EYFS. Specialist. Key stage 1. Key stage 2. Key stage 3. Key stage 4 ...
14 Recounts English ESL worksheets pdf & doc